Glaucoma is an umbrella term for a wide range of eye diseases, each of which has its own unique symptoms.
Open-angle and Closed-angle Glaucoma Are the Most Common Types.
Among the many similarities between these two forms of glaucoma are the following:
- The most significant risk factor is high eye pressure.
- Affected individuals often have impairment to the optic nerve as the defining feature of their condition.
- In addition, the following significant variations exist:
- It’s common for open-angle to have minimal symptoms, whereas closed-angle tends to have abrupt symptoms.
- Eye pressure increases gradually in open-angle viewing, but suddenly in closed-angle viewing.
Increasing eye pressure may occur as a consequence of aging, certain drugs, and even ocular injuries.
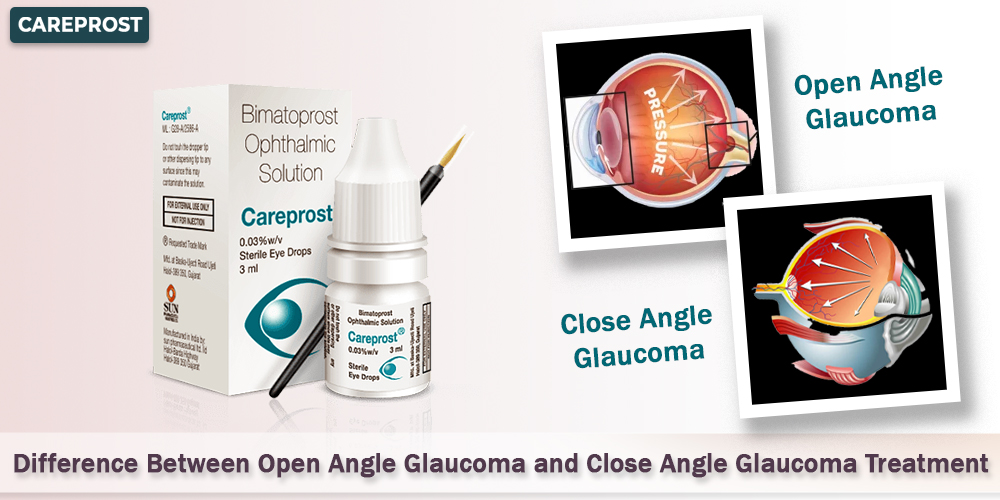
Open-angle and closed-angle forms of glaucoma may occur if high eye pressure (21mmHg or millimeters of mercury) is left untreated.
What is the Origin of the Term “Angle”?
This angle is where the eye’s aqueous humour flows into the body’s circulatory system. The correct amount of aqueous humour helps to keep the eyes at the proper pressure.
Trabecular meshwork, an internal sponge-like structure in the eye, is critical for the proper drainage function to work. Trabecular meshwork, drainage canals, collecting channels and veins are all places where fluid exits the body.
We lose the trabecular cells that assist the meshwork in its critical work as we age, which increases our chance of developing excessive eye pressure. Consequently, fluid might accumulate in the eye.
Open-angle Glaucoma – What is It?
Most persons with glaucoma are diagnosed with this version of the illness. Although the exact reason is unknown, many specialists believe that as the pressure in the eye increases, it puts more strain on the optic nerve, eventually leading to vision loss.
It’s possible to lose your vision so slowly that you won’t notice any signs of this long-term condition. It is necessary for your eye doctor to do particular diagnostic procedures in order to assess your eye pressure and determine how open the drainage angle between the iris and cornea is if you have an ongoing chronic disease, such as open-angle.
Closed-angle Glaucoma: What is It?
You should seek early treatment for this kind of glaucoma, also known as angle-closure glaucoma or narrow-angle, since it is a medical emergency. Your eye’s aqueous fluid is entirely obstructed, generating a dramatic increase in ocular pressure. If left untreated, this kind of glaucoma super lash bimatoprost may lead to complete blindness in a matter of days.
Most of the time, angle-closure glaucoma is an acute condition that must be treated immediately, even if it occurs gradually and without symptoms. Eye discomfort that is both severe and throbbing
- Eyes that are reddish-brown
- Vision is hazy.
- Headache
- Vomiting and diarrhea.
Causes
Some individuals get glaucoma for unknown reasons, while others do not. Genetics may have a role in certain instances of glaucoma, however this makes up fewer than 10% of all occurrences. Secondary glaucoma is the term for this condition.
Factors that increase the likelihood of a person
The open-angle glaucoma risk factors include:
- Growing older
- African descent has a long history of glaucoma.
- Nearsightedness
- Although low blood pressure may be dangerous, it can also pose a number of other health risks.
- Use of corticosteroids on the skin
- being plagued by an ocular tumour
- A high IOP
Closed-angle glaucoma’s risk factors include:
- The ageing process
- Femininity; Glaucoma in the family
- Diagnostic of Asian Irresponsibility
Glaucoma may be accompanied by a high IOP, however this is not always the case. 25 to 50 percent of people with glaucoma had normal IOP, according to a research conducted in 2015.
You must have your eyes dilated for a thorough eye exam in order to determine if you have open- or close-angle glaucoma. Optometrists and specialists in glaucoma will utilize a variety of tests, such as:
- An eye chart is used to measure a subject’s visual acuity.
- Peripheral vision is examined by doing a visual field test.
- Dilated eye examinations may be the most critical test. You won’t feel a thing. For a few hours, you may have trouble seeing details up close and be more sensitive to bright lights.
- Numbing drops are put in the eyes, and a particular equipment measures the pressure at or close to the cornea by an optometrist. However, you may experience a tingling sensation when your physician places the drops on your skin.
- You will have numbing drops put in your eyes before an optometrist measures the thickness of your cornea using an ultrasonic wave equipment.
- Both open- and closed-angle glaucoma treatments
You can use careprost plus eye drops. To begin, hypotensive drops are used to lower the blood pressure.
As a starting point, eye specialists will aim for a 20–50% reduction in intraocular pressure. If your eyesight continues to deteriorate, or if the doctor discovers abnormalities in the optic nerve, they will reduce the target.
Prostaglandin analogues, fatty acids present in almost all tissues, are the first line of pressure-lowering medications. The uveoscleral outlet, where aqueous humour drains, may be made more efficient by using these devices. This medication must be taken just once every night.
Additional medications that a doctor may prescribe as a last resort include:
- Agonists of the alpha kind
- Beta-blockers
- Inhibitors of carbonic anhydrase activity.
- Cholinergic agonists.
Other options include:
- Laser trabeculoplasty in a selective manner (SLT). The drainage problem is addressed and the ocular pressure is reduced using a laser directed at the trabecular meshwork. SLT has the potential to reduce blood pressure by as much as 30% on average. It works for roughly 80% of patients. In certain circumstances, SLT is being used in place of eye drops. A three- to five-year impact is possible, and the operation may be repeated at a later date.
Trabeculectomy. A new aqueous humour drainage channel is created during this procedure, which is a complicated sort of surgery.